Did you know that mass production and modern warfare had so much in common? The increased production rate to supply large armies with the current and new weaponry was the direct result of revolutionizing efficiency.
The scale of violence was unheard of in any past wars. From the most produced fighter aircraft in the shortest amount of time, the Bf-109, to the millions of Mosin Nagants still in circulation, to the iconic AK-47, these most produced weapons of warfare have caused profound shock due to the massive casualties of wartime.
The Colt Model 1911
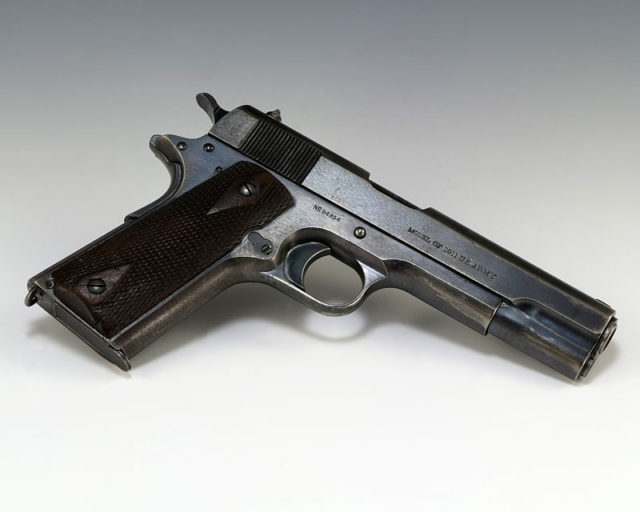

A historical pistol with a lifespan longer than any other military sidearm. It was originally designed one hundred years ago by the renowned John Browning at Colt. A very conservative estimate of at least 2 million units of the Model 1911 was produced during its lifespan. The US military used it for over 79 years and model M1911A, created in 1926, is being employed by the military today. Clients of the Colt pistol have ranged from the Soviet Union, given as aid during WW II, to Nazi Germany; many were confiscated as a result of capture, and today are found everywhere from Haiti to Luxembourg.
It has appeared in 295 movies and is probably one of the most enduring examples of engineering excellence in weapons and firearm history.
The Messerschmitt Bf-109
Originally conceived as an interceptor fighter aircraft, all later models were designed to complete several tasks, such as a fighter-bomber, a day-night-all-weather fighter, a bomber escort, a reconnaissance aircraft, and as a ground-attack aircraft. It was distributed to and maintained by several countries during World War II and performed duties with several nations for numerous years after the war.

Three German fighter aces of World War II flew the Bf-109. Among them, they claimed to have shot down 928 enemy aircraft while flying with the German Luftwaffe, mainly on the Eastern Front. Erich Hartmann of Germany was the highest scoring fighter ace of all time, credited with 352 victories and also survived the war. The Bf-109 was also flown by Hans-Joachim Marseille, claiming to have shot down 158 enemy aircraft – 154 of which were against fighter planes flown by western-trained pilots. He was the highest scoring German ace in the North African Campaign. The production of the Bf-109 was the most prolific in aviation history, with a total of 33,984 aircraft produced from 1936 to April 1945.
The Mosin Nagant
Since this Russian model bolt-action rifle was first introduced in 1891, Russian armories have manufactured an astounding 37 million Mosin Nagant rifles since.
In 1914, the Mosin Nagant was standard issue for the soldiers of the Tsar and during World War II, for the Red Army.
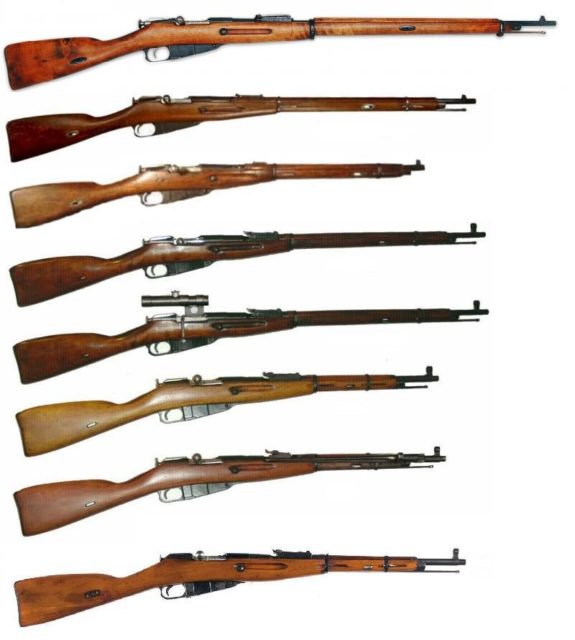

Later, for much of the Cold War, it was distributed to Moscow’s allies and Communist guerrilla movements. Recently, the now antiquated rifle has shown up in news footage coming from both Ukraine and Syria; millions are still in circulation.
The Ilyushin Il-2 Sturmovik
To the Russian pilots, the aircraft was merely the tiny ‘Ilyusha.’ To the soldiers on the ground, it was the ‘Flying Infantryman,’ the ‘Flying Tank,’ or the ‘Hunchback’ and its postwar NATO service nickname was ‘Bark.’
The Il-2 Russian fighter plane played a decisive role on the Eastern Front. In his inimitable manner, Joseph Stalin paid the Il-2 Sturmovik a great tribute. When an individual production facility fell behind on its deliveries, Stalin sent a furiously phrased message to the factory manager letting him know that the Ilyushin Il-2 Sturmovik is as essential to the Red Army as air and bread. The message demanded more aircraft production and also included a final warning!

The Ilyushin Il-2 Sturmovik was primarily a ground-attack aircraft produced in vast quantities during World War II by the Soviet Union. With production units numbering 36,183 of the Il-2 during the war and counting the production numbers of its successor, the Ilyushin Il-10, a total of 42,330 were built, making it the single most popular military aircraft unit produced in aviation history. The high number also makes it one of the largest produced piloted airplane in history.
The T-54/55 Tanks
The T-54 and T-55 tanks are a series of Russian battle tanks that were put into service at the end of World War II. The first T-54 model was demonstrated in March 1945 and went into full production in 1947.
It turned out to be the primary battle tank for armored units of the Russian Army, including the military of the Warsaw Pact countries, and the military of several other nations. The T-54s and T-55s were engaged in many of the world’s armed encounters during the latter part of the twentieth century.

The T-54/55 tank series was one of the most-produced military tanks in modern history with estimated production ranging from 86,000 to 100,000 units!! These battle tanks were later replaced by other series of armored tanks including the T-62, T-64, T-72, T-80, and T-90, but the T-54 and T-55 remain in use by up to fifty other armies in the world, some even received high-tech improvements.
The P-47
The Republic P-47 Thunderbolt aircraft was built from 1941–1945 and is driven by a powerful internal combustion engine. It is one of the heftiest and biggest fighter aircraft in aviation history. It was armed with four 50-caliber machine guns on each wing. The P-47 weighed up to eight tons when fully loaded.
When it was in the fighter/bomber mode for ground attacks, it could carry a bomb load of 2,500 pounds, as well as five-inch rockets under the wings. It could carry more than half the armament of the B-17 heavy bomber, although the B-17 had a far greater range.
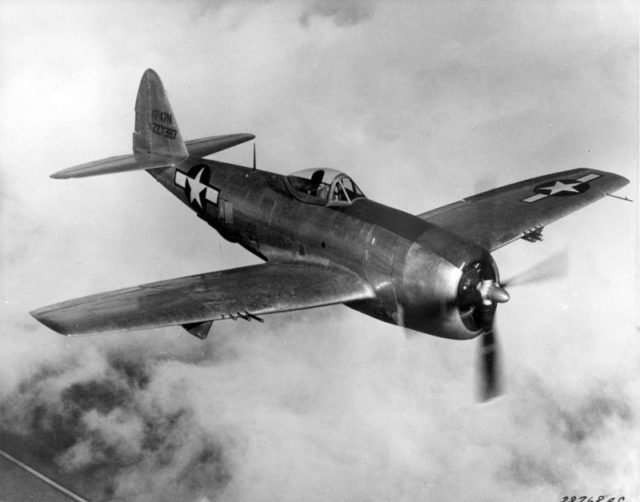

This aircraft was one of the primary fighter planes of the US Army Air Force (USAAF) in World War II. It was also in service with most of the other Allied air forces, most notably those of Russia, Britain, and France. Brazilian and Mexican fighter squadrons fighting alongside the U.S. were also equipped with the P-47.
The armored cockpit was comfortable for the pilot; it was roomy inside and offered good visibility. There were 15,660 P-47s built at the cost of US $83,000 per unit.
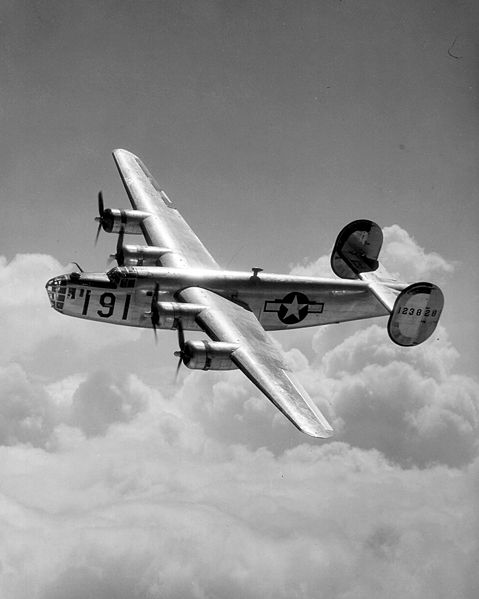
The B-24
This heavy bomber was widely used in the Second World War. It was assigned duties in every branch of the American Armed Forces and saw use in every theater of operations.
The B-24 also served admirably in the air force and navy of several Allied countries. Along with the B-17 – “Flying Fortress” – the B-24 was the backbone of the US strategic bombing operation in the Western European war theater. Because of its extended range, it proved quite valuable in bombardment operations in the Pacific, including the bombing of Japan. An estimated 19,200 rolled off American assembly lines at the cost of $297,627 –approximately $4.79 million in today’s dollars!

The Liberty Ship
The ships were constructed in an assembly line style, and made of prefabricated sections that were welded together. This method was somewhat like the technique used by Palmer’s at Jarrow, in northeast England, but the sections were welded rather than riveted. Riveted ships took the shipyards several months to build. The workforce was newly trained; mostly women who had replaced the men that were enlisting – no one had previously built welded ships.
The first ships needed 230 to 250 days to build, but the average was ultimately reduced to 42 days. The record time was set by the Robert E. Peary, which was launched four days and 15½ hours after the keel was laid. This was quite a publicity stunt and was not repeated. In fact, much of the final construction and other work remained to be completed after the Peary was launched.
In 1943, an average of three Liberty ships were completed daily. Typically, the Liberty ships were usually named after famous Americans, starting with the historic Americans who signed the Declaration of Independence. Seventeen of the Liberty Ships were named, in the 1940s, in honor of outstanding African-Americans.
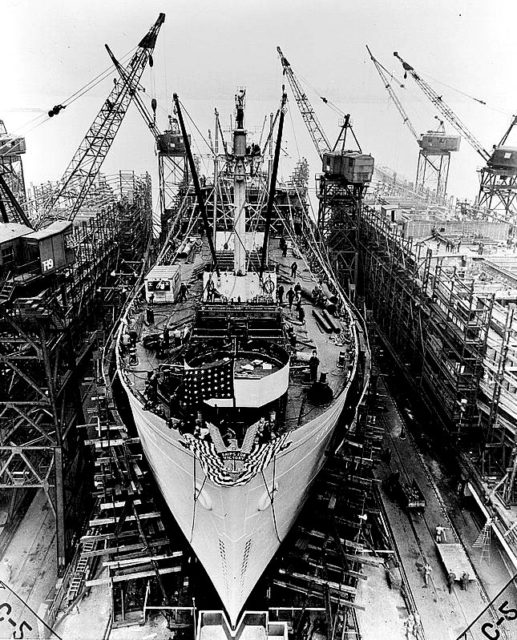
The first was christened by Marian Anderson in 1942, in honor of Booker T. Washington; the SS Harriet Tubman, acknowledging the only woman on the list was launched on June 3, 1944. In all, over 2,700 Liberty ships were built during the Second World War.
The Kalashnikov
The Avtomat Kalashnikov (AK) design work began during the last year of the Second World War.
In 1946, the AK-47 was submitted for official military assessment and in 1948, the fixed-stock form was presented for active service with selected troops of the Russian Army. An early new advancement of the design was the AKS, which was equipped with an under-folding metal shoulder stock.

The AK-47 was officially recognized by the Soviet Armed Forces in 1949. The assault rifle was used by the majority of the member states of the Warsaw Pact.
Read another story from us: A Nuclear weapon that has been missing since 1950 might have been found
It’s been almost seven decades and the AK-47 model and its variations remain widely used and the most popular assault rifle in the world. Why? Because of its availability in virtually every geographic region, lower production costs compared to contemporary Western weapons, considerable reliability under harsh conditions, and ease of use. Over 100 MILLION have been manufactured and are being used all over the world!
