The Yahi tribe was a group of indigenous Native American people that used to populate the Deer Creek region in California. Belonging to the Yana group of people, the Yahi believed all persons are equal and so lived with no main political authorities.
Divided into groups, the Yahi use to hunt and gather for their food. The nation consisted of 400 people who lived isolated from the outer world and fought fiercely to defend their territory, which was close to the Californian land mines.
The Yahi were the first to experience the consequences of the gold rush. When more than 300,000 people from all around the United States came to California in their search for the precious metal, the territory of the Yahi became overwhelmed by the hostile gold miners. The Yahi fought against the settlers but were eventually annihilated due to their lack of guns. A series of massacres decreased the numbers of the indigenous tribe to less than 100 people.
With the rivers occupied by the gold diggers and the decreased number of deer in the forests, the Yahi lost their hunting spots and lived in starvation. In 15 years, the white men had managed to wipe out the entire tribe. The remaining 16 members of the Yahi hid in the mountains, and for many years, not a single member of the Yahi tribe could be seen in California. At least not until 1911, when the last Yahi unexpectedly appeared in the civilized world.
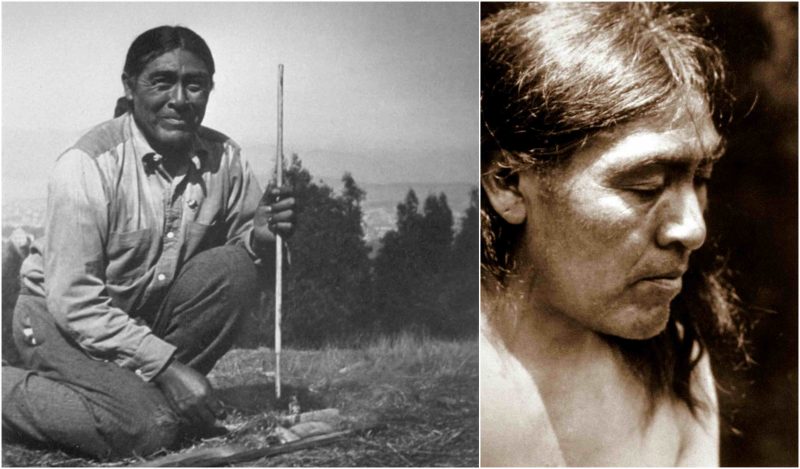
On 29th August 1911, a middle-aged Native American was captured while searching for food, who later proved to be the last member of the Yahi tribe. The man who was around 50 years old wouldn’t tell his name to his captors, as per the old Yahi tradition not to reveal their names to the enemy. After being released from custody, the Yahi was taken to California University in San Francisco, where he would stay until his death. The man who became an instant sensation was named Ishi by the university anthropologists Alfred Kroeber and Thomas Waterman. Ishi simply stands for “men” in the Yana language, and as years passed, the ill-fated man accepted this name.
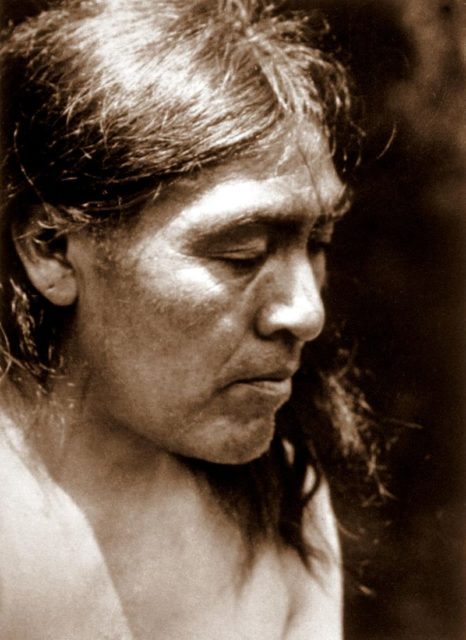

Ishi ran into the wilderness with some members of his tribe after the massacre of 40 of his tribesmen in 1865. Around 33 members of the Yahi tribe managed to escape, of which half were shot dead very soon after. Ishi remained in hiding for 44 years until a group of surveyors found their camp in 1908. Ishi and his relatives managed to escape, all but his sick mother. When Ishi returned to the camp, he found only his mother there, who died shortly after. The other relatives never returned, so he remained alone and spent the next 3 years wandering in the forests looking for food. In 1911, the desperate and starving man finally revealed himself to the modern world.
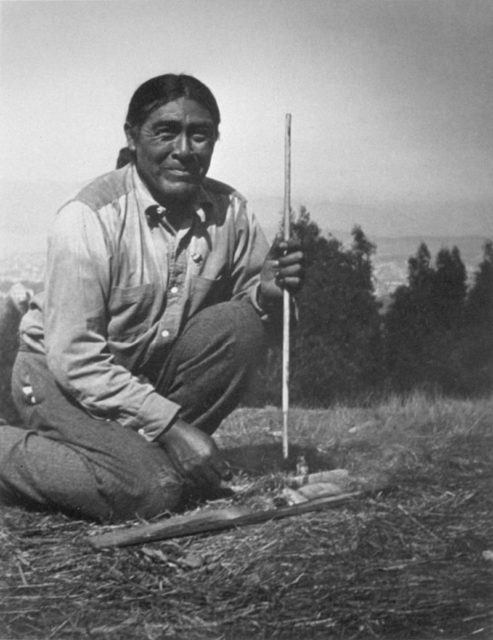

When Ishi was captured, the authorities wanted to send him to the Indian Reservation in Oklahoma, but Alfred Kroeber insisted that Ishi remain at the university. They got him an apartment near the university museum and studied him for several years. Ishi managed to learn around 600 English words and taught the anthropologists about Yahi culture and the Yana language.
He was employed at the university as a research assistant and worked constantly in the museum. Ishi was practically displayed for the visitors of the museum, and he would spend his days showing the little children how to make bows and arrows. During those years, Ishi and the employees at the university became friends. He became especially close with Saxton Pope, who was Ishi’s doctor and who was fascinated by Ishi’s skills. In 1914, Ishi and his friends made an excursion to the Yahi natural habitat, where Ishi presented his tracking and hunting skills.

As a man who had spent most of his life outside the civilized world, Ishi was not immune to the modern diseases around him and became ill very often. Only five years after he became a member of the western society, Ishi got sick from tuberculosis and consequently died on 25 March 1916. His friends tried to prevent an autopsy of his body to keep his body intact, as per the Yahi customs, but their efforts were in vain.
Read another story from us: Fascinating photos of Apache Native Americans from the 1890s to the 1920s
The autopsy went ahead, and the doctors at the University of California removed Ishi’s brain, before cremating his body. The remains of the last Yahi were buried at Mount Olivet Cemetery near San Francisco. His brain was sent to the Smithsonian Institution in Washington by Ishi’s friend Alfred Kroeber. The brain remained there until 10 August 2000, when it was given to descendants of the Pit River Tribe, who buried the brain and Ishi’s ashes on a secret location in the Deer Creek region.
