A country’s navy is one of its most important military branches, and to be successful, it needs powerful ships to battle with. In the 17th century, the Royal Swedish Navy commissioned the construction of what was to be their greatest warship yet, the Vasa. However, before it could see any action, the massive ship sank, only to be recovered centuries later and serving as the only fully intact warship of its time to be salvaged.
Construction of the Vasa
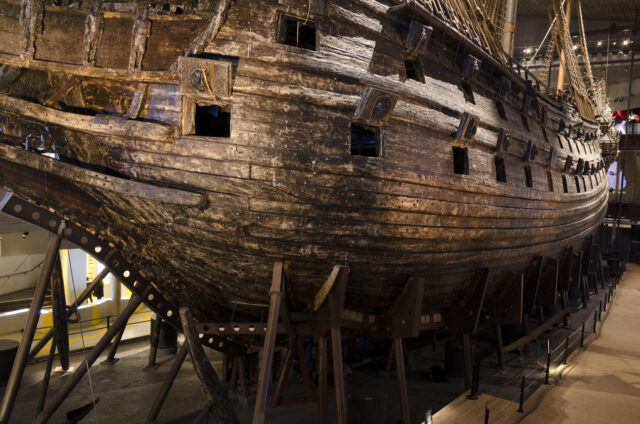

During the 1620s, Swedish king Gustavus Adolphus ordered the construction of a new warship to serve his people’s defence. The name Vasa was chosen for the warship and it was hastily constructed to provide the Swedes with more power and protection against the now-historic bi-confederation entity reigned by one monarch, the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, whom they were waging war with.
Upon its creation, the Vasa warship was described with several superlatives such as being the greatest and most capable war vessel at the disposal of the Swedish navy. The ship came to symbolize Sweden’s Great Power Period, a time when the Nordic country controlled most of the Baltic Sea and forged its status as one of Europe’s most powerful kingdoms.
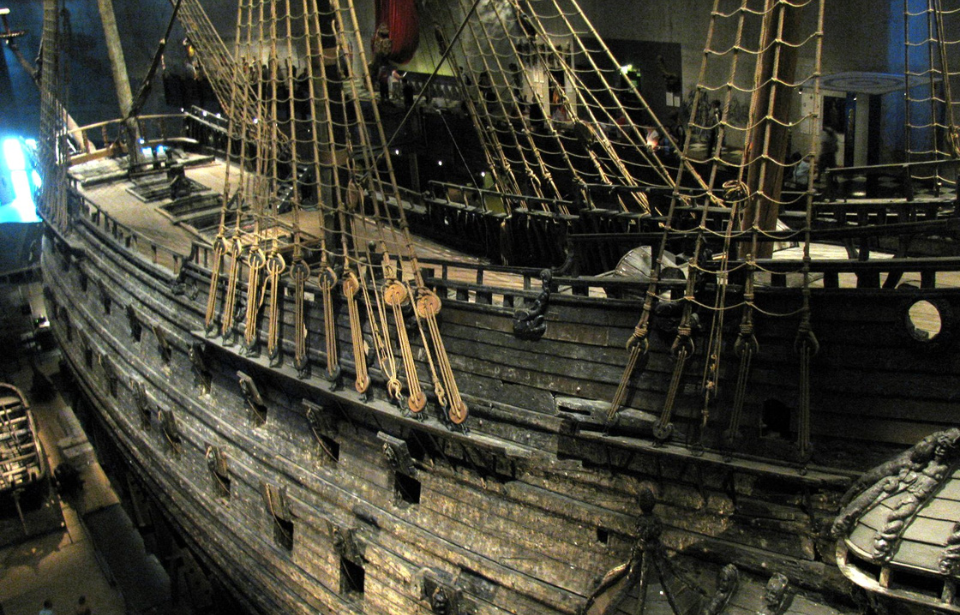
The ship’s appearance was stunning, measuring 226 feet in length, 164 feet in height, and weighing more than 1,200 tons. With some 64 cannons installed on it, it promised whoever tried to mess with Vasa would face serious consequences. As it turned out, it never came to that.
The Vasa and the Titanic
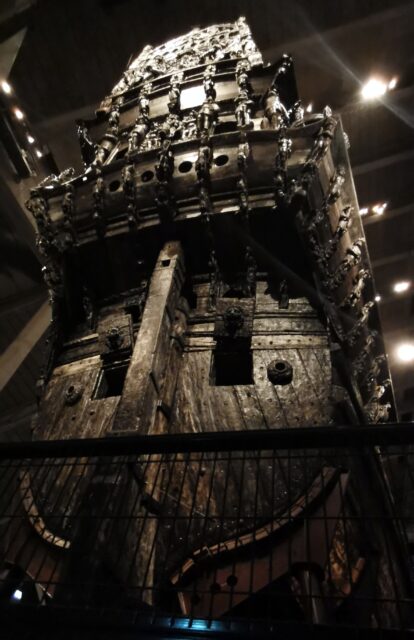

The ship, against everyone’s expectations, proved to be fallible and faced an end that might easily remind people of the story of the RMS Titanic. While Vasa did not hit an iceberg but still ignominiously sunk on its very first journey. It was an embarrassing incident, overseen by crowds of Swedes who had gathered at the port of Stockholm from where the ship set sail towards the open seas for the very first and last time on August 10, 1628. About 30 of the 150 people onboard drowned as a result of the sinking.
Scattered throughout the onlooking crowd were prominent guests, including royals and ambassadors from other countries. Everyone was excited to see the great ship off, but after having sailed not even one nautical mile, the mighty warship suddenly plunged into the water.
What caused the Vasa to sink?

Accounts point to errors happening during construction. The contract was signed early in the year 1625, with Vasa being one of four vessels agreed to on the list by Dutch shipbuilder Henrik Hybertsson. The original arrangement was to have two smaller vessels and two bigger vessels, but sadly Hybertsson died shortly after undertaking the project. As such, the construction effort was taken over by his assistant, Hein Jakobsson.
Plans were modified during construction, as Vasa, which was intended to be one of the two smaller ships, appeared to be fitting the pair of two bigger ships upon completion. By the time it was completed, the ship was much heavier than planned. It also carried extra weights such as hundreds of sculptures and at least 100 tons of ballast.
More evidence shows that the Swedes had the warship tested and noticed something was wrong with it, but under the pushy demands of the king, Vasa was prematurely sailed into the open sea and towards its premature doom. A strong gust of wind was enough to overturn the vessel. When water began to enter, all it took was a few minutes for it to sink 105 feet below the surface.
Moving on from its sinking
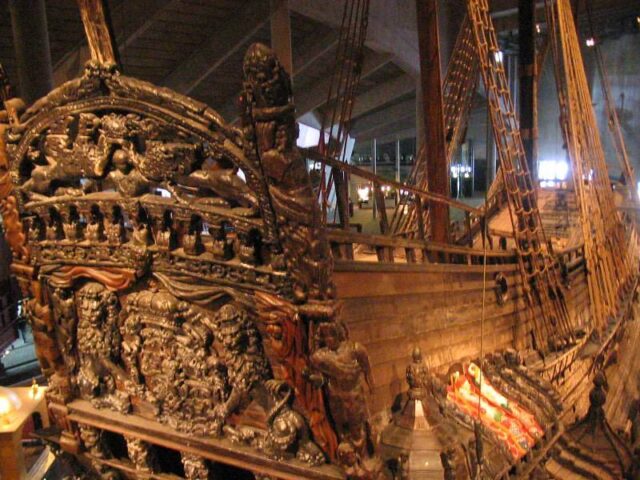
The Swedes were quick to dismiss and forget Vasa. This was to be their new favorite war toy, their national pride and joy, yet it now lay sunk on the bottom of the ocean on its maiden voyage. It was a scandal that hurt the reputation of the kingdom, as well as having huge economic repercussions: Vasa had cost a fortune.
While an investigation was ushered in immediately after the ship sank, little could be done, especially considering that the main shipbuilder had already been dead for over a year. There were some efforts to recover Vasa from the sea floor, but the task seemed impossible with the limited technology of the time. By the 1660s, a group of divers was able to retrieve the cannons, using an early model of the diving bell. However, the shipwreck was eventually left abandoned and forgotten until the mid-20th century.
Rediscovering Vasa
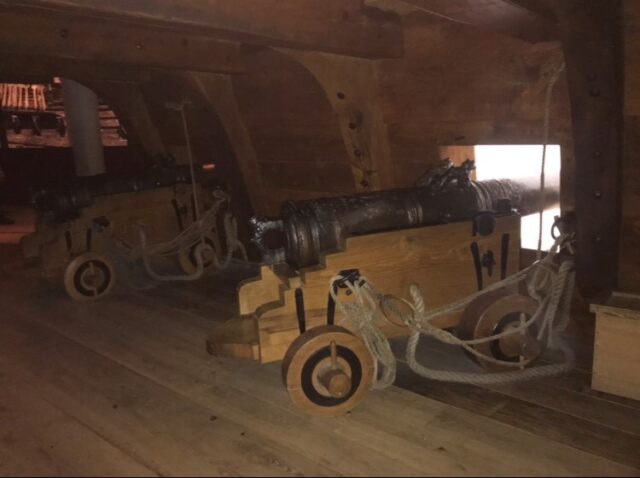

In 1961, a few years after the shipwreck was rediscovered and identified as the lost 17th-century Vasa vessel, Sweden finally managed to recover it. Although she had remained submerged in the sea for centuries, upon its reappearance, it seemed to be in positively pristine condition.
The underwater position where it had sunk was key to its preservation. The water was dark enough to stop ultraviolet light from protruding and affecting the ship’s wood and the chilly temperature of the Baltic was soothing, preventing any rapid deterioration processes. Additionally, having sunk close enough to the harbor, there was enough pollution in the water to bleach most parasites that may have wanted to feast on the wood of the wreck.
Vasa on land

There were some decaying issues once the ship was taken out of the water. The great ship had undergone some restoration processes early on, such as being treated with substances to protect the wood, but lab research later confirmed that the wood of the ship was struggling with extremely slow, ongoing fiber degradation. While there is no threat of immediate collapse, this issue has remained a major occupation for conservationists who are still looking for the best way to stop the risky process.
Read another story from us: Incredibly Well-Preserved 16th Century Warship Discovered
Should the Vasa museum where the shipwreck is famously displayed in Stockholm allow its prime exhibit to perish for the second time, it would be a huge national loss. The Vasa serves as a relic of a time long gone and has a special history with the Swedes as well as being one of the best preserved historical ships in all of the world.
